Early man lived in this country from the oldest stages of the stone age. His pre-sence attested by the discovery of numerous deposits of stone implements and other remains in caves and rock-shelters on the northern and eastern mountains
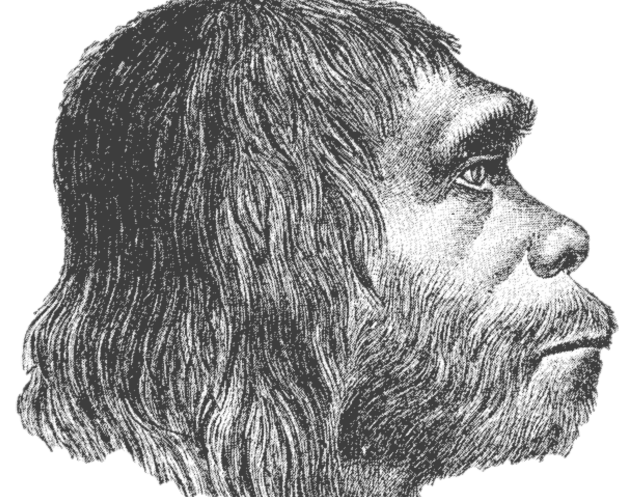


Early man lived in this country from the oldest stages of the stone age. His pre-sence attested by the discovery of numerous deposits of stone implements and other remains in caves and rock-shelters on the northern and eastern mountains
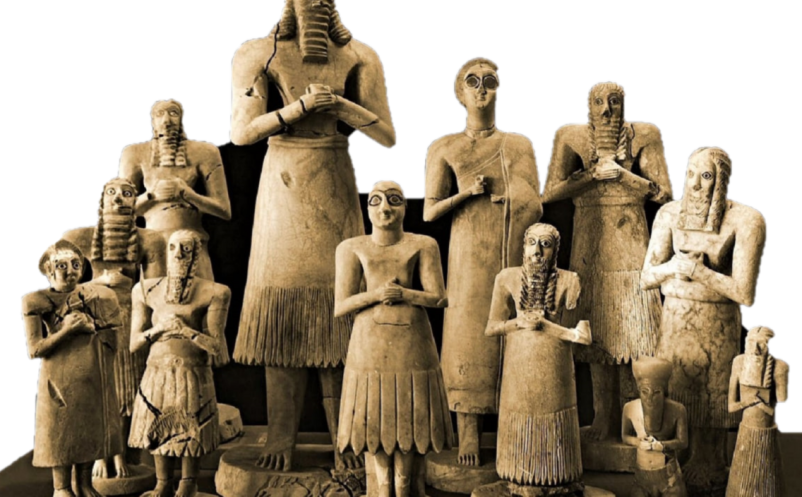

Towards the beginning of the third millennium B.C., a few dynastic states emerged in various cities of South Mesopotamia, each consisting of an independent city-state ruled by a king. Simultaneously, writing was further developed and became more suitable for keeping records and conveying information.

Sargon of Akkad (2340-2284 B.C. )𒈗𒁺
came to power at Kish and rallied around him an strong army of Semitic speakers of Akkadian. To consolidate his hegemony over Sumer, Sargon sacked the neighbouring cities and launched a military campaign against Lugal-zaggesi, King of Uruk,
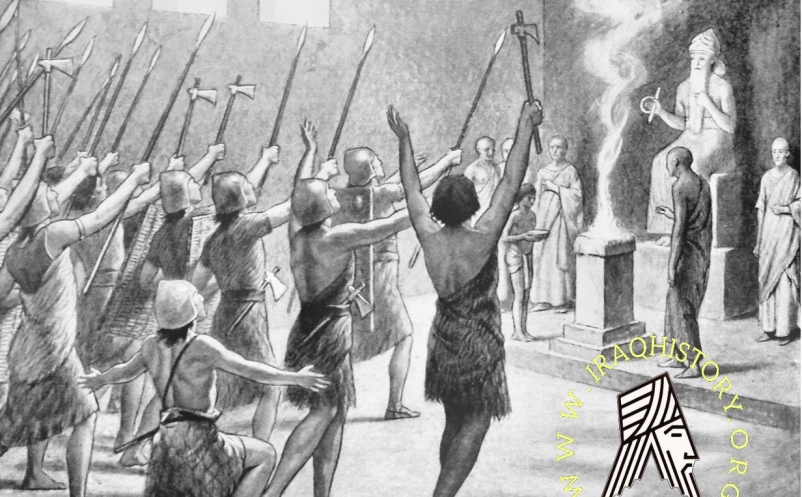

The Guti (2210-2116 B.C.) were mountain nomads who descended to the plains of Mesopotamia (ca. 2210 B.C.) from the slopes of the Zagros and from the borders of Luris- tan.
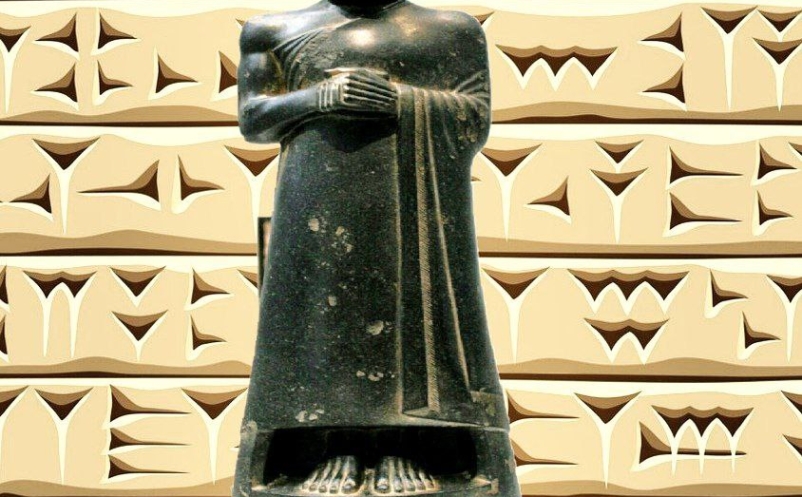

Unstable condition under the last phase of Guti rule enabled the Sumerians to re-sein their independence. Several of the southern cities re established their autonomy,
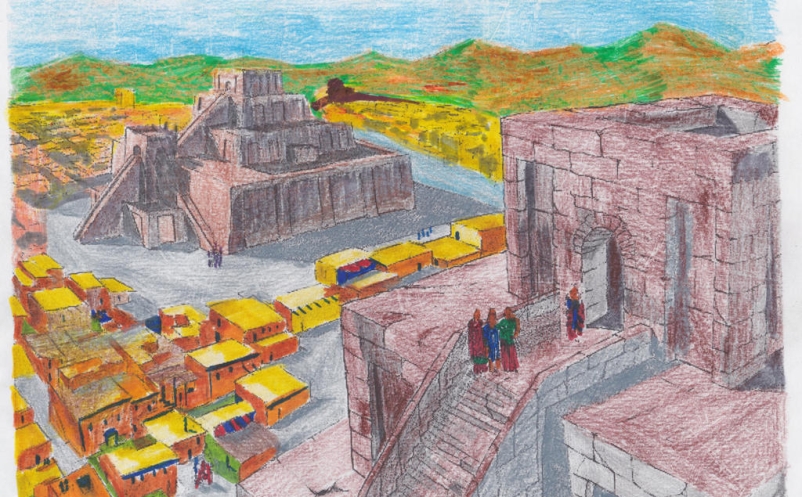

OLD BABYLONIAN PERIOD
Following the downfall of the 3rd Dynasty of Ur and the withdrawal of the Ela mites, several independent city states emerged; among them Isin and Larsa. Other new kingdoms were founded at Babylon, Uruk Eshnunna and Ashur and in the city of Mari a new independent dynasty came to power.
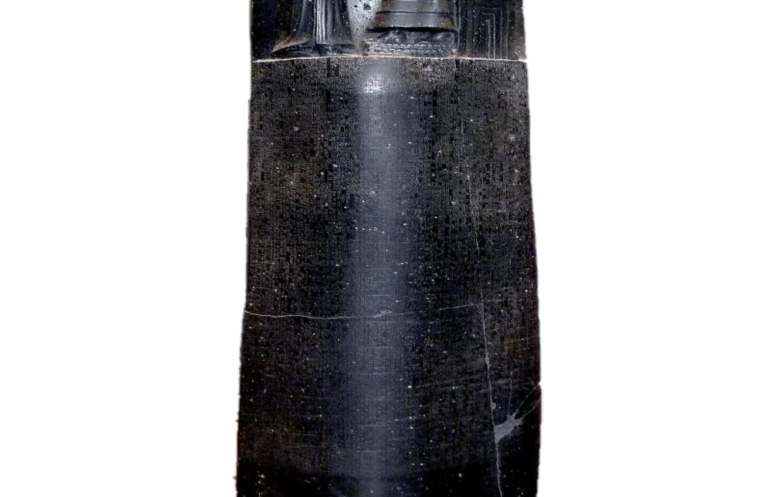

The first dynasty of Babylon, also called the Amorite Dynasty, comprises eleven reigns with a total duration of three centuries (1894-1594 B.C.). In that time, the civilization of Iraq reached a peak of glory and radiated to other peoples of the Near East
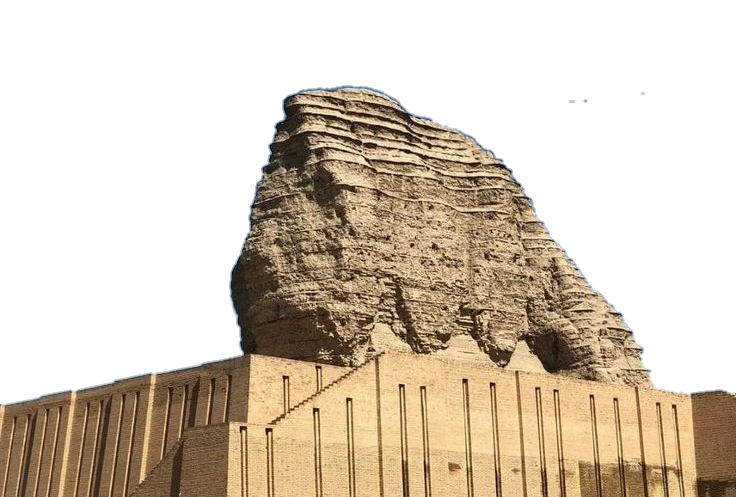

THE KASSITES(c. 1680-1157 B.C.)
The Kassites, led by their king Gandash (c. 1680-1665 B.C.) descended from thelnorth-eastern range of mountains an area known today as Luristan.
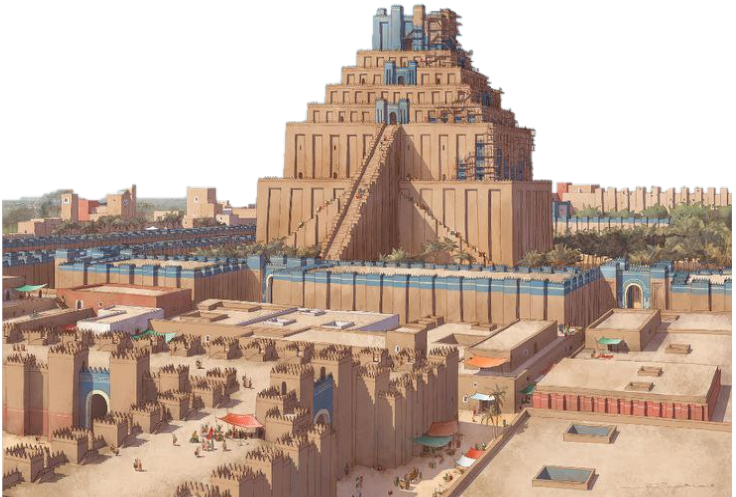

Following the downfall of the Kassites, local rulers seized power in Babylon and southern Iraq, each attempting to assert his independence in his own city.
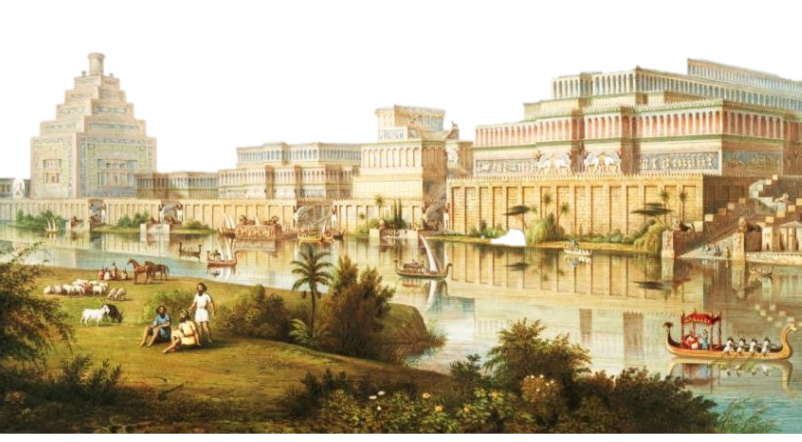

The Assyrians are a Semitic people which settled in the northern part of Mesopotamia in the third millennium B.C. The earliest
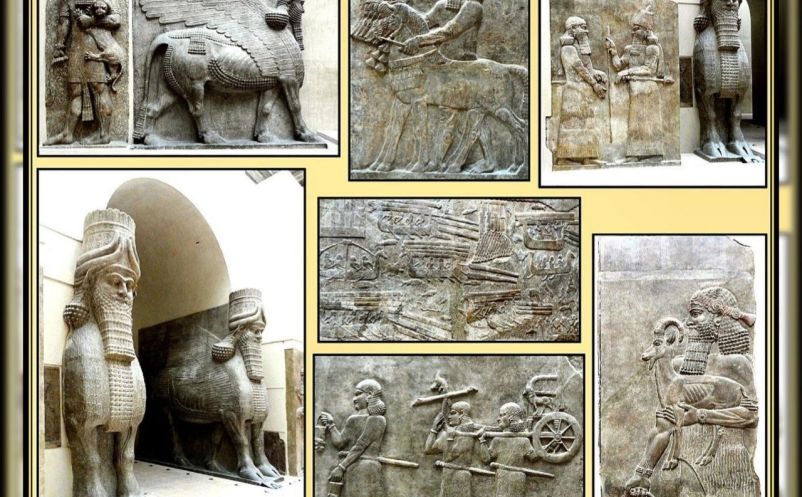

The first obstacle which the Neo-Assyrian kings had to surmount was the resistance of Aramaean tribes which had settled in territory close to the heartlands of Assyria Itsel Gradually the Aramaeans were subjected and their kingdoms in North Mesopotamia
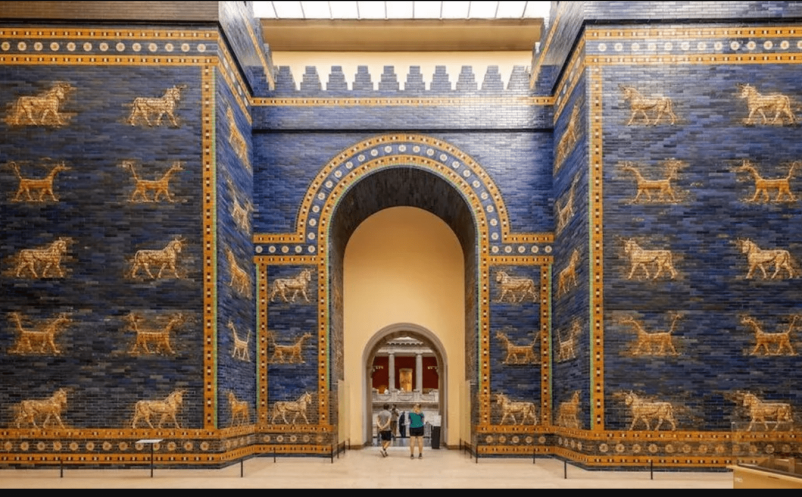

Nabopolassar (626-605 B.C.) was the founder of the Chaldaean or Neo-Babylonian Dynasty, and in collaboration with the Medes was responsible for the downfall of the As syrian Empire, which he shared with the Median king…

THE ACHAEMENID (PERSIAN) EMPIRE (550-331 B.C.) At the time of their earliest appearance in history the Achaemenid Persians were subject to the Median kings of northern Iran. Under their king Cyrus the Persians fought a…
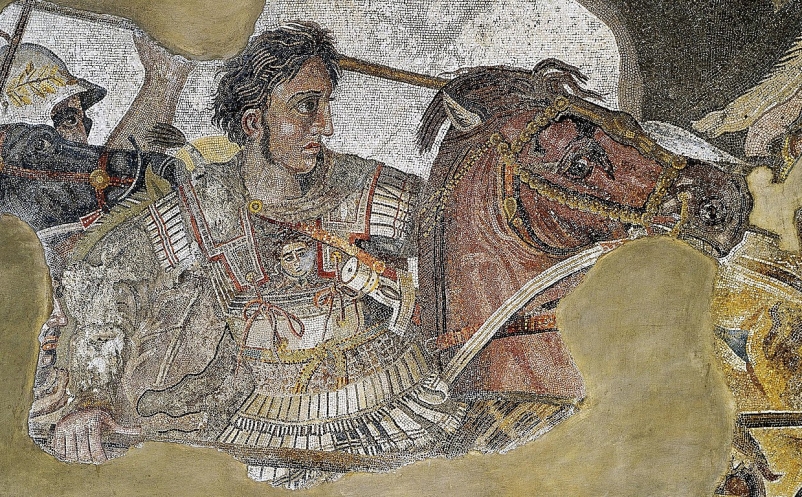

ALEXANDER THE GREAT (334-321/323 B.C.) Alexander’s father, King Philip of Macedon, had gone a long way towards achie ving the union of all the provinces of mainland Greece and the islands, and at the time…
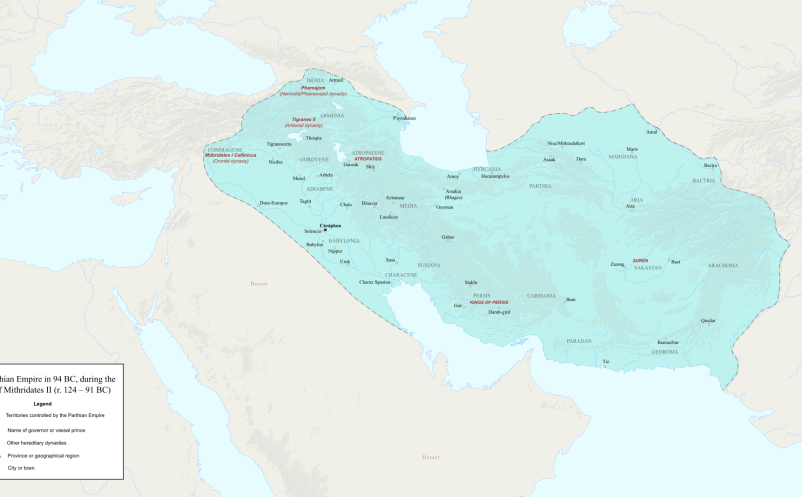
PARTHIAN PERIOD (In Iraq: 139 B.C. 226 A.D.) The Parthians seem to have first made thier appearance in history in northeasterm Iran, and from there broke through towards the south and west. Under their leader…

THE SASSANIAN PERIOD (226-637 A.D.) Ardashir (226-241 A.D.), was the son of of Babek and the grandson of Suman, fr whom the dynasty is named. During the Parthian period the rulers had been hig constantly…
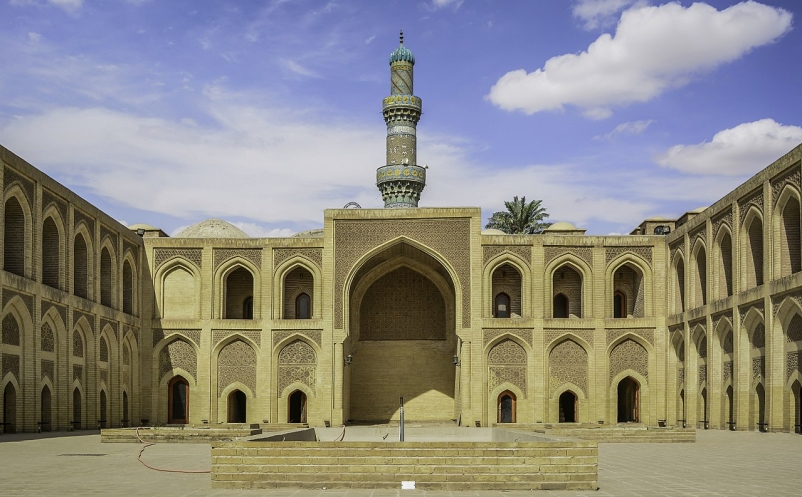

THE ARABS AND ISLAM In Pre-Islamic times the Arabs had established kingdoms and pefly states not only in the Arabian Peninsula but in Syria and fraq as well. In particular they founded cities in the…